In this ultimate guide, you’ll learn everything about the Panama Shift Pattern, including how to implement it, the benefits it can bring, and the challenges you may face.
What is a Panama shift pattern?
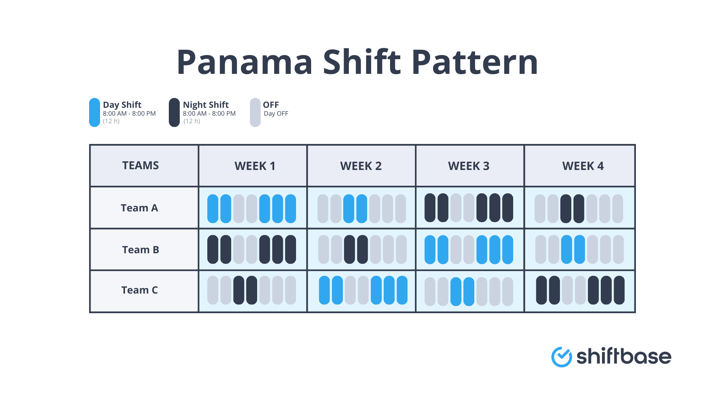
Imagine a work schedule where your team works fewer days, gets regular long breaks, but still keeps the business running 24/7. That’s the Panama shift pattern in a nutshell.
This pattern is built around teams working 12-hour shifts in a repeating two-week cycle. It’s common in manufacturing, security, healthcare, energy, and other 24/7 operations.
Typical 2-week rotation
| Week | Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
- ✅ = Work (12-hour shift)
- ❌ = Off
How it works
- Week A: 2 days on, 2 off, 3 on (2-2-3)
- Week B: 2 off, 2 on, 3 off (mirror of Week A)
- Across 14 days employees work 7 shifts (7 × 12 = 84 hours) → ~42 hours/week on average.
👀 Worth noting: Employees often get a long weekend every other week—great for planning. The trade-off is the 12-hour day, which can be fatiguing in high-intensity roles.
Tip for managers: Watch for signs of fatigue and enforce breaks. Rotate tasks where possible.
What is the Panama Plus schedule?
Panama Plus is a variation that adds one extra 8-hour weekday shift every two weeks for training, admin, team meetings, or catch-up work.
- Typical average becomes ~46 hours/week (7 × 12h + 1 × 8h over 2 weeks).
- Plan that 8-hour shift in advance and—if possible—let staff choose the day.
Example with the extra shift
| Week | Mon | Tue | Wed | Thu | Fri | Sat | Sun |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | 🕗 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
- 🕗 = Extra 8-hour shift
- ✅ = 12-hour shift
- ❌ = Off
⚠️ Heads-up: Even one extra day can affect work–life balance. Communicate early and schedule fairly.
Panama vs. Panama Plus at a glance
| Feature | Panama | Panama Plus |
|---|---|---|
| Shifts per 2 weeks | 7 × 12h | 7 × 12h + 1 × 8h |
| Avg hours/week | ~42 | ~46 |
| Consecutive days off | Up to 3 | Usually 2–3 |
| Built-in training/admin | Not built-in | Included (8h) |
| Fatigue risk | Moderate | Slightly higher |
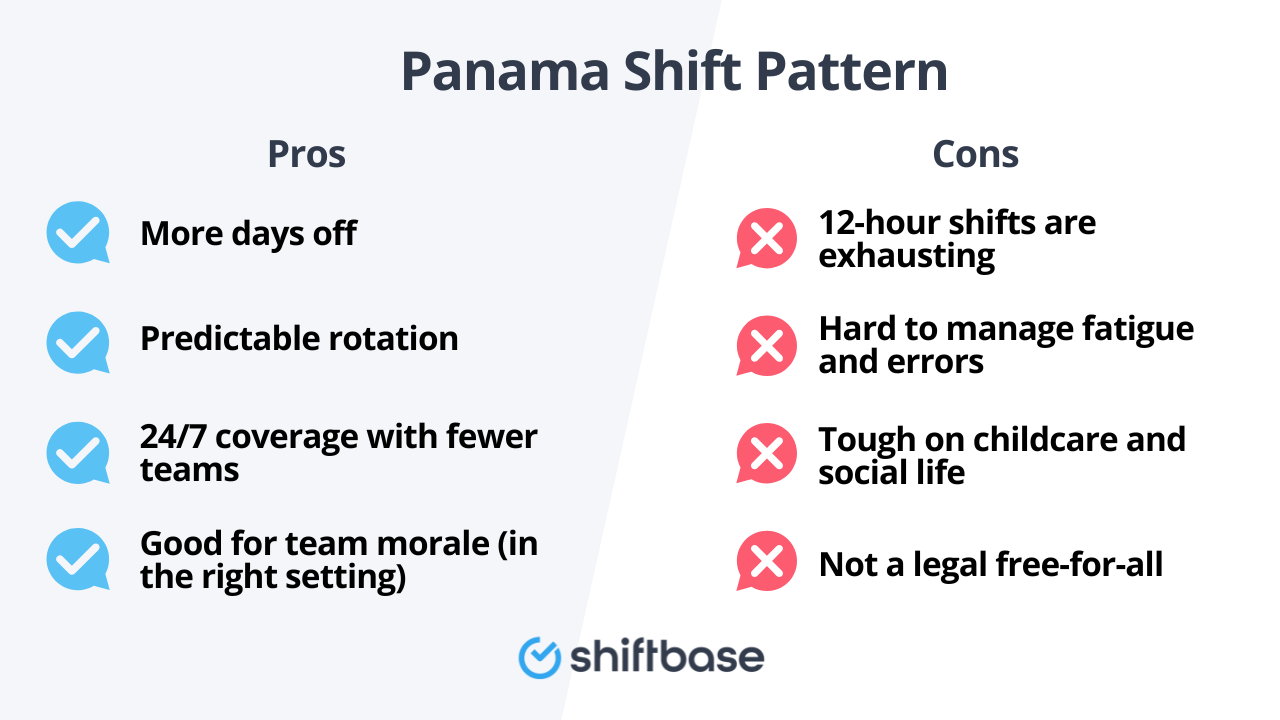
Pros and cons of the Panama shift pattern
✅ Pros
- More days off: 7 off days every 2 weeks, with regular 3-day weekends.
- Predictable rotation: Easy to plan holidays, training, and rotas.
- 24/7 coverage with fewer teams: Typically 4 teams can cover round-the-clock.
- Morale boost (in the right setting): Extended breaks suit many 24/7 environments.
❌ Cons
- 12-hour shifts are tiring: Especially in safety-critical or physically demanding work.
- Fatigue/error risk: Performance dips late in the shift—strong break policies needed.
- Family logistics: Rotations can clash with childcare and social routines.
- Compliance isn’t automatic: UK Working Time Regulations still apply (see below).
Legal considerations for the Panama shift pattern (UK)
Panama can work brilliantly for 24/7 operations—but you must align with the Working Time Regulations 1998 (WTR).
| Rule | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Maximum weekly hours | 48 hours/week on average over a 17-week reference period (unless the worker has opted out in writing). |
| Daily rest | At least 11 consecutive hours of rest between working days. |
| Weekly rest | At least 24 hours off each 7 days, or 48 hours off each 14 days. |
| Rest breaks during shifts | At least a 20-minute uninterrupted break if working more than 6 hours. |
| Night work limits | Night workers’ average daily hours must not exceed 8 hours in any 24-hour period averaged over the reference period. A hard 8-hour limit can apply to work involving special hazards or heavy physical/mental strain. |
📌 Note: A standard Panama pattern averages ~42 hours/week (Panama Plus ~46). Overtime or swaps can push averages up—monitor carefully before relying on opt-outs.
Opt-out agreements (the 48-hour rule)
- Use opt-outs only if averages would exceed the 48-hour limit; they must be voluntary and can be withdrawn with notice.
- Keep signed opt-outs on file; don’t pressure staff to sign.
Contracts, consultation, and records
- Ensure contracts reference shift work and the pattern/flexibility.
- Consult employees or representatives—especially if changing existing rotas; check any collective agreements.
- Keep working time records (hours, breaks, night work, opt-outs) for at least two years.
Health & safety
- Assess risks linked to long/overnight shifts; rotate duties where possible.
- Offer free health assessments for night workers.
- Make reasonable adjustments if health is affected by the shift schedule.
Tip: Use time & attendance tools to track hours and avoid accidental breaches.
Who typically uses the Panama shift pattern?
The Panama pattern suits 24/7 operations where round-the-clock coverage matters:
Manufacturing & production
- Why it works: Continuous production, minimal downtime, predictable staffing across four teams.
- Example: A bottling plant runs control rooms and lines 24/7 with four rotating crews.
Healthcare & emergency services
- Why it works: Consistent cover for urgent care, balanced with regular multi-day breaks.
- Example: A private urgent care clinic reduces burnout by ensuring every other weekend off.
Security & law enforcement
- Why it works: Fair, predictable coverage for sites and control rooms; fewer handovers.
Utilities & energy
- Why it works: Control rooms and plants need qualified staff on at all hours.
Logistics & distribution
- Why it works: Keeps hubs and warehouses moving without constant overtime.
Does this suit office teams?
Rarely. Panama is built around long, fixed shifts and in-person coverage—less suitable for desk-based or hybrid roles.
Best practices for implementing the Panama shift pattern
1. Get buy-in early
- Explain benefits: More days off, predictable rotation.
- Be honest: 12-hour shifts are demanding.
- Gather feedback: Short survey/Q&A; involve works councils/union reps where relevant.
2. Pilot before rollout
- Trial with one team for 1–2 months.
- Track attendance, overtime, productivity, incident rates, and complaints.
- Collect anonymous feedback mid-pilot and adjust.
3. Update contracts & policies
- Reference the pattern/flexibility in contracts.
- Document bank holiday, overtime, and pay rules for long shifts.
- Align time-off, sick leave, and absence policies to the rota.
4. Stay compliant
- Check the pattern against WTR (averages, rest, night work).
- Use a checklist or rota software to avoid breaches.
5. Support health & wellbeing
- Schedule proper meal and rest breaks.
- Rotate duties where possible; provide fatigue management training.
- Offer night-worker health checks.
6. Use smart scheduling tools
- Automate Panama-style rotations and flag compliance risks.
- Sync hours to payroll; give employees self-service access.
⏱️ Shiftbase templates handle Panama, DuPont, and other rotating patterns out of the box.
7. Communicate clearly
- Share a clear visual calendar of the 2-week rotation.
- Explain how holidays, bank holidays, and swaps work.
- Create a living FAQ for common questions.
Panama shift pattern alternatives
2-2-3 (a.k.a. Panama/Pitman)
Often used interchangeably with “Panama.” Same 2-week 2-2-3 cadence and 12-hour shifts.
DuPont schedule
A 4-week cycle mixing 12-hour days/nights. Includes a full week off each cycle—great for morale but more complex to manage.
Continental shift
A 7-day rotation of 8-hour shifts (mornings/evenings/nights). Less intense than 12-hour days but more frequent handovers.
Pitman (2-3-2)
Another popular 2-week pattern: 2 on, 2 off, 3 on, then 2 off, 2 on, 3 off. Balanced rest; still needs 4 crews for 24/7.
How to choose?
- Do you need full 24/7 coverage?
- Can your team realistically handle 12-hour shifts?
- Fixed shifts or rotating?
- Do you have software to manage complexity and compliance?
Tip: Trial with one team for a month, gather feedback, and refine.